题目
给定一个含有 n 个正整数的数组和一个正整数 target 。
找出该数组中满足其和 ≥ target 的长度最小的 连续子数组 [numsl, numsl+1, …, numsr-1, numsr] ,并返回其长度。如果不存在符合条件的子数组,返回 0 。
示例 1:
输入: target = 7, nums = [2,3,1,2,4,3]
输出: 2
解释: 子数组 [4,3] 是该条件下的长度最小的子数组.
示例 2:
输入: target = 4, nums = [1,4,4]
输出: 1
示例 3:
输入: target = 11, nums = [1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1]
输出: 0
提示:
- 1 <= target <= 109
- 1 <= nums.length <= 105
- 1 <= nums[i] <= 105
分析
这道题一开始想到的是暴力解法,也就是把每种可能的子数组长度都试一遍,后来发现这是道典型的滑动窗口题目,用滑动窗口就解决了。之后看官方题解有前缀+二分搜索的方法作为扩展。
代码
滑动窗口
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
if (nums.length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int left = 0, right = 0;
int s = nums[0];
int windowLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (right < nums.length - 1) {
// 右指针移动
while (s < target && right < nums.length - 1) {
right++;
s += nums[right];
}
// 左指针移动
while (s >= target) {
windowLen = Math.min(windowLen, right - left + 1);
s -= nums[left];
left++;
}
}
return windowLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : windowLen;
}
方法很简单,就是一个左指针,一个右指针,窗口的范围就是2个指针之间的元素。
一开始先移动右指针直到窗口内和大于等于target
然后向右开始移动左指针,直到窗口内和小于target,由于每次就是一次满足s≥target的窗口,我们就要每次和当前的窗口长度进行比较从而找到最小的窗口长度,也就是最小的子数组长度。
如果窗口长度为最大的int值说明没有找到任何一个满足s≥target的窗口,返回0。
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是数组的长度。指针最多各移动n次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
前缀+二分搜索
public int minSubArrayLen(int target, int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
int windowLen = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int[] sums = new int[n + 1];
// 前i个数之和
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sums[i] = sums[i - 1] + nums[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int s = target + sums[i];
// 二分搜索
int bound = Arrays.binarySearch(sums, s);
// bound为负数表示找不到,返回的是插入位置,且从1开始
if (bound < 0) {
bound = -bound - 1;
}
// 找到最小的
if (bound <= n) {
windowLen = Math.min(windowLen, bound - i);
}
}
return windowLen == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : windowLen;
}
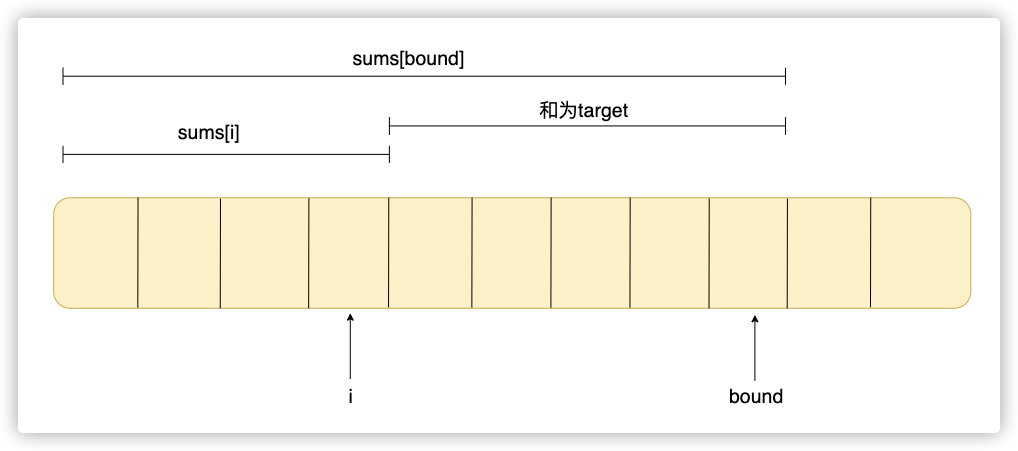
这个方法我们先计算出nums中不同长度的前i个数之和的数组sums,也就是sums[i]表示nums[0]到nums[i-1]中的所有数之和。
然后我们用二分查找在sums数组中找到下标bound,使得sums[bound]-sums[i]>=target,且这个bound是所能找到的最小的。(由于nums都是正整数,sums一定是递增的,所以可以用二分搜索)
最终bound-i就是我们要找的最小的窗口长度。
- 如果找到关键字,则返回值为关键字在数组中的位置索引,且索引
从0开始 - 如果没有找到关键字,
返回值为负的插入点值,所谓插入点值就是第一个比关键字大的元素在数组中的位置索引,而且这个位置索引从1开始。
贴个这个工具类的源码:
private static int binarySearch0(long[] a, int fromIndex, int toIndex,
long key) {
int low = fromIndex;
int high = toIndex - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) >>> 1;
long midVal = a[mid];
if (midVal < key)
low = mid + 1;
else if (midVal > key)
high = mid - 1;
else
return mid; // key found
}
return -(low + 1); // key not found.
}
复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度:O(nlogn),其中n是数组的长度。需要遍历每个下标作为子数组的开始下标,遍历的时间复杂度是 O(n),对于每个开始下标,需要通过二分查找得到长度最小的子数组,二分查找得时间复杂度是 O(logn),因此总时间复杂度是 O(nlogn)。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是数组的长度。额外创建数组 sums 存储前缀和。
![Featured image of post [leetcode]209.长度最小的子数组](/p/min_sub_array_len/leetcode_hua465350402cd0ec3eacd50007e571132_103033_800x0_resize_box_3.png)